Root Canal
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
A root canal
is a procedure to remove diseased pulp from your tooth. The pulp is tissue that contains nerves and blood vessels that fill your tooth roots. Each root secures your tooth to your gum and jawbone. You may need a root canal if your tooth is damaged or infected. An abscess (pocket of pus), cavities, or an accident or injury can also lead to a root canal.
How to prepare for a root canal:
- Your dental provider will tell you how to prepare for your procedure. He or she will use x-rays to examine the area. The pictures will show how bad the infection is and help your provider know the size and shape of the root canals. You will be given local anesthesia to prevent pain during the procedure. You may also be given antibiotics to help prevent an infection caused by bacteria.
- If you have a filling or other dental device on your tooth, your dental provider will remove it. A rubber sheet will be put around your tooth. The sheet helps prevent saliva from entering the root canal. It also helps prevent you from breathing in or swallowing liquids or small tooth pieces. Your provider may remove the crown on your tooth with a dental drill. He or she may also drill a hole in the crown to reach the pulp and root canal.
What happens during a root canal:
- Your dental provider will insert tools into the root canals. The tools will remove the diseased pulp from the tooth with cleaning fluids. An x-ray may be taken to check for more pulp to remove. Your provider will clean any remaining pulp from the root canal. After all of the pulp is removed, he or she will clean the open root canal with germ-killing liquid. The root canal will be dried and a filling will be put inside your tooth root.
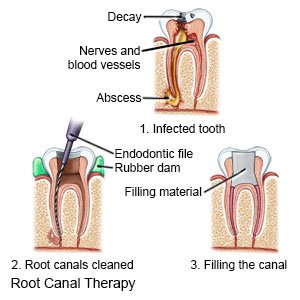
- Your dental provider will cover your tooth with a temporary or permanent crown. He or she may fill the root with a steroid paste to relieve any swelling in the root canal.
What happens after a root canal:
You may have some pain after your procedure. This is normal and should go away in a few hours. Your dental provider may prescribe pain medicine or recommend an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as an NSAID. Ask your provider when you can eat and drink again. Ask about any special instructions for caring for your tooth after a root canal. If a temporary crown is used, your provider will replace it with a permanent crown about 1 week later.
Risks of a root canal:
The cleaning fluid used to clean the root may enter nearby tissues and cause swelling, bruising, or an infection. The tip of a dental tool may get stuck in your root canal, or you may swallow the tip if it drops into your mouth. You may get a fistula (abnormal tissue opening) between your tooth root and your sinus. The diseased tissue may not be completely removed. The root may not be completely filled, or the seal may not be tight. This means germs could enter your tooth and cause an infection. You may need another root canal, or your tooth may need to be removed.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have increasing pain in or around your tooth that does not go away with pain medicine.
- You have new or increased swelling in your gums or face.
- You have tooth pain that spreads up to your gums and cheek.
Contact your dentist or endodontist if:
- You have a fever.
- Your new filling or crown falls out or feels like it is out of place.
- Your tooth cracks or breaks.
- Your tooth hurts when you bite down.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Self-care:
- Care for your teeth as directed. This may help prevent cavities, tooth injuries, and other tooth problems. Visit your dental provider regularly to have your teeth cleaned and checked.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause blood vessel damage and delay healing. Ask your dental provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
Follow up with your dentist or endodontist as directed:
You may need to return to have your temporary crown replaced with a permanent crown. You may also need more tests to make sure your tooth is healing. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
